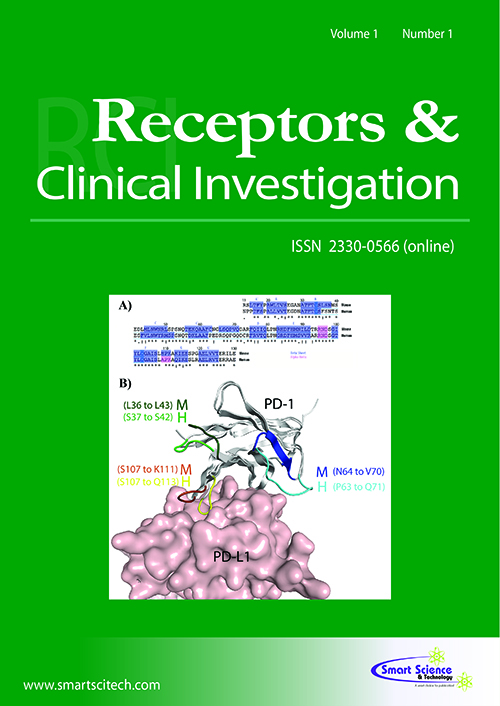
EphB and ephrinB in pain signaling
Abstract
The Ephrin type B receptors (EphB) and their membrane bound ephrinB ligands are involved in diverse facets of cell physiology and pathophysiology. EphB-ephrinB signaling mediates synapse formation and plasticity by regulating the insertion, localization and function of glutamate receptors in synaptic membranes. Whereas, EphB-ephrinB signaling at the excitatory glutamatergic synapses in the dorsal horns of the spinal cord, has been implicated in the pathophysiology of pain. Here, the key evidence that support the participation of EphB-ephrinB signaling in pain processes are highlighted. Then, a possible role for the pseudokinase EphB6 in the EphB-ephrinB pain signaling complex is considered. These pathways are currently being intensely studied to exploit selective therapeutic targets for pain relief.